View
백기선님의 스프링 프레임워크 핵심 기술이라는 강좌를 들으며 공부한 내용을 정리한 글입니다.
스프링 초기에는 컨테이너나 bean을 xml로 설정하는게 대세였지만, 많은 개발자들의 의견을 수용하여 Annotation 기반의 DI를 지원하기 시작했다. 따라서 손쉽게 Bean을 등록하고 사용할 수 있게 되었다.
이번 글은 xml을 이용한 Bean 등록 방법부터, 현재 많이 사용되고 있는 Annotation기반 Bean 등록 및 사용 방법까지 공부한 내용을 정리한 내용이다.
public class TestServcie {
TestRepository testRepository;
public void setTestRepository(TestRepository testRepository) {
this.testRepository = testRepository;
}
}
public class TestRepository {
....
}
우선 TestService와 TestRepository를 만들고 이를 이용해 다양한 Bean 등록 방법에 대해 살펴보자. 먼저 고전적인 방법인 xml을 통해 Bean을 등록하고 주입하는 방법이다.
1. xml 설정 파일에 Bean 등록하기
Springboot 프로젝트를 생성하면 다음과 같은 클래스가 만들어진다.
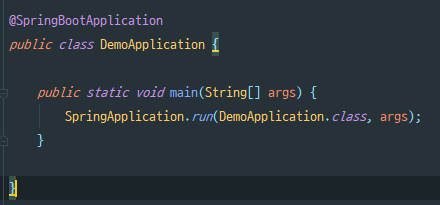
Bean 등록이 잘 이루어지는지 확인하기 위해 먼저 @SpringBootApplication 이라는 Annotation을 지워준다. (@SpringBootApplication이 어떤 역할을 하는지는 마지막에 설명)
그리고 Bean 설정 파일인 xml을 만들어준다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="testService"
class="me.study.springapplicationcontext.TestServcie">
</bean>
<bean id="testRepository"
class="me.study.springapplicationcontext.TestRepository">
</bean>
</beans>
이런 식으로 TestService와 TestRepository를 bean으로 등록할 수 있다.
하지만 이렇게 bean 등록만 해주는 것으로는 TestService가 TestRepository를 주입받을 수 없다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="testService"
class="me.study.springapplicationcontext.TestServcie">
<property name="testRepository" ref="testRepository"/>
</bean>
<bean id="testRepository"
class="me.study.springapplicationcontext.TestRepository">
</bean>
</beans>
이처럼 property를 통해 TestRepository를 주입받을 수 있다.
- name은 TestService에 setter를 통해 가져오는 값
- ref는 레퍼런스로 다른 bean을 참조한다는 의미
- setter로 들어갈 수 있는 bean의 id 값이 와야 한다.
- 즉, testRepository라는 id를 가진 Bean을 참조하겠다는 의미
이제 의존성 주입이 잘 되었는지 간단한 테스트를 통해 확인해보자.
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
String[] beanDefinitionNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(beanDefinitionNames));
TestServcie testService = (TestServcie) context.getBean("testService");
System.out.println(testService.testRepository != null);
}
}
등록된 bean들을 가져오고 testService의 testRepository가 null이 아닌지 체크를 해본다.

실행시켜보면 true가 출력이 되고 testRepository가 null이 아니라는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
즉, 의존성 주입이 잘 되었다는 것이다.
하지만 이 방법은 일일이 bean으로 등록해야 한다는 엄청난 귀찮음을 동반한다.
그래서 등장한게 context의 component-scan이다.
2. component-scan
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="me.study.springapplicationcontext"/>
</beans>
base-package에 명시된 패키지부터 bean을 스캐닝을 해서 등록을 하겠다는 의미이다.
Component라는 Annotation(@Component)을 이용해서 bean으로 등록할 수 있다.
예를 들면, @Service라는 Annotation은 @Component를 확장한 Annotation이다.


이처럼 Annotation을 명시하는 것 만으로 손쉽게 Bean을 등록할 수 있게 되었다.
Annotation을 스캐닝해서 bean 등록 및 설정을 해주는 Annotation 기반의 방법은 스프링 2.5부터 사용할 수 있는 기능이다.
그런데 이 방법 말고 Bean 설정 파일은 Java 기반으로 작성할 수 없을까? 해서 나온 방법이 바로 Java 설정 파일이다.
3. Java Configuration
Java Class 파일을 만들고, @Configuration Annotation을 명시하면
"이 Java 파일은 Bean 설정 파일이다."라는 의미를 가지게 된다.
@Configuration
public class ApplicationConfig {
@Bean
public TestRepository testRepository() {
return new TestRepository();
}
@Bean
public TestService testService() {
TestService testService = new TestService();
testService.setTestRepository(testRepository());
return testService;
}
}
이처럼 @Bean을 이용해서 bean을 등록하고 의존성 주입을 해줄 수 있고 xml 파일보다 좀 더 유연한 bean 설정을 할 수 있게 된다.
이렇게 설정한 Java bean 설정 파일을 어떻게 사용할까?
ApplicationContext에 아까 만든 Java Configuration 클래스를 등록해주면 된다.
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ApplicationConfig.class);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(beanDefinitionNames));
TestService testService = (TestService) context.getBean("testService");
System.out.println(testService.testRepository != null);
}
}
그렇게 되면, ApplicationConfig의 class 파일의 @Bean을 읽고 그 안에 정의된 bean을 등록하고 사용하게 된다. 그런데, 이 방법 또한 xml 파일처럼 @Bean을 사용해 일일이 bean을 등록해줘야 한다.
xml 파일보다 더 귀찮은데? 라고 생각할 수도 있다.
하지만 여기에도 xml 파일처럼 Component-scan이 있기 때문에 걱정할 필요가 없다.
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = DemoApplication.class)
//@ComponentScan(basePackages = "me.study.springapplicationcontext")
public class ApplicationConfig {
}
@ComponentScan Annotation을 사용해서 basePackage를 지정해주면 모든 클래스의 Annotation을 찾아서 Bean으로 등록하게 된다.
basePackages는 직접 패키지명을 작성하게 되어있다. 따라서 Type safe 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
basePackageClasses는 Application 클래스가 위치한 곳을 명시하기 때문에 조금 더 Type safe 하다고 할 수 있다.
우리는 ApplicationContext를 직접 만들어서 사용하지 않고 있고, 사실 위에 작성한 ApplicationCofig 파일도 필요 없다. Spring boot Project에서는 이러한 기능을 기본적으로 제공하고 있다. 처음에 @SpringBootApplication Annotation을 지운 이유이다.

@SpringBootApplication은 기본적으로 ComponentScan과 Configuration을 가지고 있기 때문에, 이 자체가 Bean 설정 파일인 것이다.
여태까지 Springboot를 사용하면서 내부 동작에 대한 이해 없이 그냥 가져다 쓰기만 한 것 같다. 이번 강의를 통해 Bean들이 어떻게 등록되고 관리되는지, IoC의 전반적인 이해를 높일 수 있었다. 또한 지금까지 사용하던 Annotation들의 의미를 조금이나마 알게 된 것 같다.
다음에는 의존성 주입 방법 중 하나인 @Autowired에 대해 학습하고 정리한 내용을 올릴 예정이다.
'BackEnd > Spring 핵심 기술' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [스프링 핵심기술] - MessageSource (0) | 2020.06.04 |
|---|---|
| [스프링 핵심기술] - Bean의 스코프 (0) | 2020.05.28 |
| [스프링 핵심기술] - @Component와 @ComponentScan (0) | 2020.05.17 |
| [스프링 핵심기술] - @Autowired (0) | 2020.05.12 |
| [스프링 핵심기술] - Ioc 컨테이너와 Bean (1) | 2020.05.09 |
